上篇中,我们分析了 webpack 是如何处理自编译同步加载的,本篇中我们来分析 webpack 是如何处理模块打包和加载的。
示例项目:https://github.com/njleonzhang/deep-into-webpack-output-sample
我们还是使用上篇中那个简单的例子, 只不过这次我们把它编译成模块:
// const.js
export let name = 'leon'
export default function print() { console.log('print: ' + name) }
exports.default = {
entry: './const.js',
mode: 'development',
devtool: 'cheap-module', // 为了让打包后的模块更好阅读
output: {
filename: 'index.dist.js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, './dist/'),
library: 'MyLibrary',
libraryTarget: 'umd' // 依次使用 'var', 'commonjs', 'commonjs2', 'amd', 'umd'
},
}
模块打包
首先, 我们来观察 webpack 对不同 libraryTarget 的处理, libraryTarget 决定的模块导出类型有三大类: 作为变量导出, 作为对象导出 以及 作为模块导出, 官网上有详尽的介绍, 这里我结合实例来看几个典型的情况。
余文中,
_entry_return_代表模块的导出, 后文中会给出具体实例。
作为变量导出
libraryTarget: 'var'
library: 'MyLibrary'
var MyLibrary = _entry_return_;
很容易理解,在这种情况下导出模块的输出被直接复制给了一个变量。具体到我们的例子,编译出来的代码为 index.var.js.
定睛一看这代码,就是上篇中我们分析的那些嘛,我们隐去 webpack 启动代码的部分:
var MyLibrary = /******/ (function(modules) {
/******/
// ... webpack 启动代码
return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = "./const.js");
/******/ })
/************************************************************************/
(
// 各模块的代码
{
"./const.js": (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports__);
/* harmony export (binding) */ __webpack_require__.d(__webpack_exports__, "name", function() { return name; });
/* harmony export (binding) */ __webpack_require__.d(__webpack_exports__, "default", function() { return print; });
let name = 'leon'
function print() { console.log('print: ' + name) }
})
}
)
很显然 const.js 的 模块导出(_entry_return_) 为模块自调函数的执行结果,即:
{
name: 'leon',
print: function() {
console.log('print: ' + name)
}
}
那么整个模块就相当于:
var MyLibrary = {
name: 'leon',
print: function() {
console.log('print: ' + name)
}
}
作为对象导出
libraryTarget: "window"
library: 'MyLibrary'
window['MyLibrary'] = _entry_return_;
libraryTarget: "commonjs"
library: 'MyLibrary'
exports['MyLibrary'] = _entry_return_;
将模块导出为一个对象的属性,和作为变量导出类似。
作为模块导出
经典的 cmd, amd 和 umd 3 种导出方式, 虽然 esm 的模块方案已经成为主流,但是浏览器里跑不了啊,目前来说还是个人感觉还是编译成 umd 最方便。
libraryTarget: 'commonjs2'
library: 'MyLibrary' // 会被忽略
module.exports = _entry_return_;
libraryTarget: 'amd'
library: 'MyLibrary'
define('MyLibrary', [], function() {
return _entry_return_;
});
libraryTarget: 'umd'
library: 'MyLibrary'
(function webpackUniversalModuleDefinition(root, factory) {
if(typeof exports === 'object' && typeof module === 'object')
module.exports = factory();
else if(typeof define === 'function' && define.amd)
define([], factory);
else if(typeof exports === 'object')
exports['MyLibrary'] = factory();
else
root['MyLibrary'] = factory();
})(typeof self !== 'undefined' ? self : this, function() {
return _entry_return_;
});
加载模块
现在通过 npm 我们可以安装和使用大量的第三方模块,那么 webpack 是如何处理这些模块的呢?
前文中我们把 Const.js 编译成了各种格式,我们用以下代码来加载它们:
// index.js
import Const1, { name as name1 } from '../output/dist/index.cmd.js'
import Const2, { name as name2 } from '../output/dist/index.umd.js'
import Const3, { name as name3 } from '../output/dist/index.amd.js'
import Const4, { name as name4 } from '../output/dist/index.cmd2.js'
import Const5, { name as name5 } from '../output/dist/index.var.js'
window.Const1 = Const1
window.Const2 = Const2
window.Const3 = Const3
window.Const4 = Const4
window.Const5 = Const5
console.log(Const1, Const2, Const3, Const4, Const5)
console.log(name1, name2, name3, name4, name5)
先预览一下浏览器运行的结果:
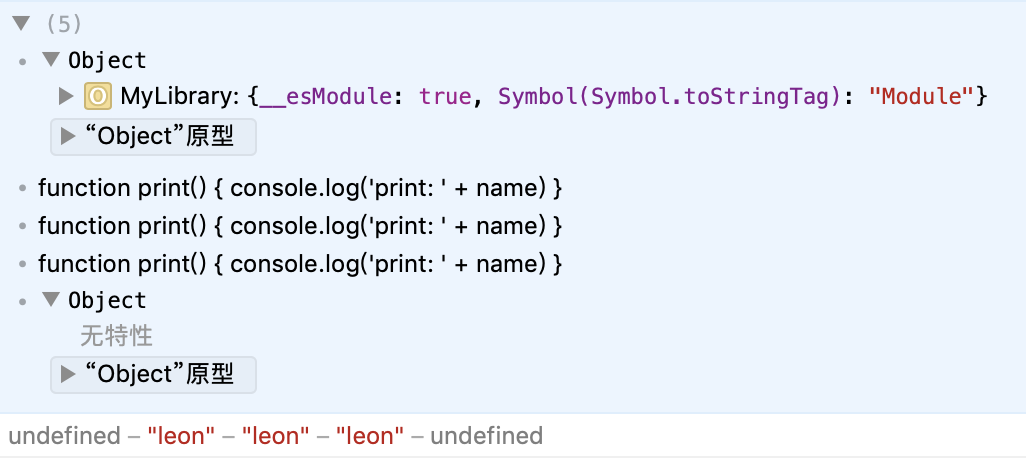
可以发现,只有导出格式为 作为模块导出 的 commonjs2, amd 和 umd 的时候,模块才能被正常解析,这是怎么回事呢?我们来看一下生成的代码
生成代码的大结构自然还是和上篇介绍的是一致的:
/******/ (function(modules) {
/******/
// ... webpack 启动代码
return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = "./index.js");
/******/ })
/************************************************************************/
(
{
"../output/dist/index.amd.js": (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) { ... }),
"../output/dist/index.cmd.js": (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) { ... }),
"../output/dist/index.cmd2.js": (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) { ... }),
"../output/dist/index.umd.js": (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) { ... }),
"../output/dist/index.var.js": (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) { ... }),
"index.js": (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) { ... }),
},
)
amd 的导入处理
以下代码是从 完整的生成代码 中截取,看的时候可以和 index.amd.js 被 import 前的代码对照一下.
/***/ "../output/dist/index.amd.js":
/***/ (function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
var __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_ARRAY__, __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__;!(__WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_ARRAY__ = [], __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__ = (function() { return /******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap
/******/ // The module cache
/******/ var installedModules = {};
/******/
/******/ // The require function
/******/ function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
/******/
/******/ // Check if module is in cache
/******/ if(installedModules[moduleId]) {
/******/ return installedModules[moduleId].exports;
/******/ }
/******/ // Create a new module (and put it into the cache)
/******/ var module = installedModules[moduleId] = {
/******/ i: moduleId,
/******/ l: false,
/******/ exports: {}
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Execute the module function
/******/ modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__);
/******/
/******/ // Flag the module as loaded
/******/ module.l = true;
/******/
/******/ // Return the exports of the module
/******/ return module.exports;
/******/ }
/******/
/******/
/******/ // expose the modules object (__webpack_modules__)
/******/ __webpack_require__.m = modules;
/******/
/******/ // expose the module cache
/******/ __webpack_require__.c = installedModules;
/******/
/******/ // define getter function for harmony exports
/******/ __webpack_require__.d = function(exports, name, getter) {
/******/ if(!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) {
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, name, { enumerable: true, get: getter });
/******/ }
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // define __esModule on exports
/******/ __webpack_require__.r = function(exports) {
/******/ if(typeof Symbol !== 'undefined' && Symbol.toStringTag) {
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, Symbol.toStringTag, { value: 'Module' });
/******/ }
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, '__esModule', { value: true });
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // create a fake namespace object
/******/ // mode & 1: value is a module id, require it
/******/ // mode & 2: merge all properties of value into the ns
/******/ // mode & 4: return value when already ns object
/******/ // mode & 8|1: behave like require
/******/ __webpack_require__.t = function(value, mode) {
/******/ if(mode & 1) value = __webpack_require__(value);
/******/ if(mode & 8) return value;
/******/ if((mode & 4) && typeof value === 'object' && value && value.__esModule) return value;
/******/ var ns = Object.create(null);
/******/ __webpack_require__.r(ns);
/******/ Object.defineProperty(ns, 'default', { enumerable: true, value: value });
/******/ if(mode & 2 && typeof value != 'string') for(var key in value) __webpack_require__.d(ns, key, function(key) { return value[key]; }.bind(null, key));
/******/ return ns;
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules
/******/ __webpack_require__.n = function(module) {
/******/ var getter = module && module.__esModule ?
/******/ function getDefault() { return module['default']; } :
/******/ function getModuleExports() { return module; };
/******/ __webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter);
/******/ return getter;
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call
/******/ __webpack_require__.o = function(object, property) { return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(object, property); };
/******/
/******/ // __webpack_public_path__
/******/ __webpack_require__.p = "";
/******/
/******/
/******/ // Load entry module and return exports
/******/ return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = "./const.js");
/******/ })
/************************************************************************/
/******/ ({
/***/ "./const.js":
/*!******************!*\
!*** ./const.js ***!
\******************/
/*! exports provided: name, default */
/***/ (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports__);
/* harmony export (binding) */ __webpack_require__.d(__webpack_exports__, "name", function() { return name; });
/* harmony export (binding) */ __webpack_require__.d(__webpack_exports__, "default", function() { return print; });
let name = 'leon'
function print() { console.log('print: ' + name) }
/***/ })
/******/ })}).apply(exports, __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_ARRAY__),
__WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__ !== undefined && (module.exports = __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__));;
/***/ })
中介的核心的自调函数是没变的,它返回的依然是上文中提到的 _entry_return_, 即:
{
name: 'leon',
print: function() {
console.log('print: ' + name)
}
}
我们把上面的代码简化下,可以示意性的缩写为:
// 示意性的缩写
"../output/dist/index.amd.js": (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
var __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_ARRAY__, __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__;
!(
__WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_ARRAY__ = [],
// 执行模块
__WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__ = function() {
return _entry_return_
}.apply(exports, __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_ARRAY__)
// 拿到执行了的结果,赋值给这个包装后的模块
__WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__ !== undefined && (module.exports = __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__)
)
})
所以在处理 index.amd.js 时, Webpack 识别出来此模块为 amd 的格式,然后把模块的里核心代码拿出来进过包装放到了加载后的代码里。我们看一下运行后 amd 模块是这样的:
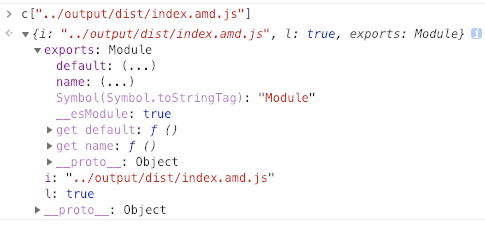
commonjs 的导入处理
commonjs 的处理比较简单,直接赋值
// 示意性的缩写
"../output/dist/index.cmd.js": (function(module, exports) {
exports["MyLibrary"] = _entry_return_
})
运行后 commonjs 模块是这样的:
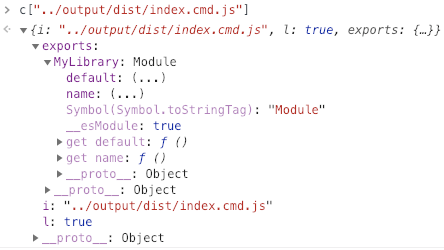
注意 commonjs 导入的时候
MyLibrary这个变量被保留了,这使得按 commonjs 打出来的包,并不能在 webpack 工程里被正常使用。
commonjs2 的导入处理
// 示意性的缩写
"../output/dist/index.cmd2.js": (function(module, exports) {
module.exports = _entry_return_
})
运行后 commonjs2 模块是这样的:
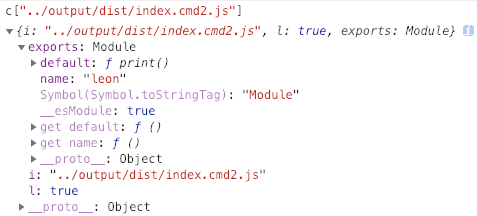
umd 的导入处理
// 示意性的缩写
"../output/dist/index.umd.js": (function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
(function webpackUniversalModuleDefinition(root, factory) {
if(true)
module.exports = factory();
else {}
})(window, function() {
return _entry_return_
})
})
运行后 umd 模块是这样的:
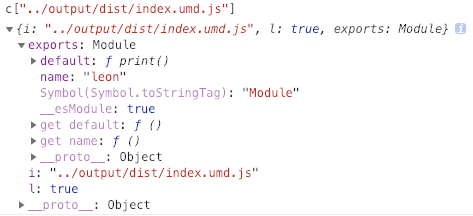
var 的导入处理
"../output/dist/index.var.js": (function(module, exports) {
var MyLibrary = _entry_return_
})
可以预见,此模块完全是不可用的:

模块的调用
最后我们来看一下 index.js 里的代码,我们从生成的代码里截取出 index.js 的代码,总体还是很好理解的和上篇介绍的差不多,都是通过 __webpack_require__ 来加载模块,不同之处在于 这次涉及 __webpack_require__.n 的使用。
/***/ "./index.js":
/***/ (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
// 为模块打上 esModule 标记
__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports__);
// 加载 index.cmd.js 并 读取 其 default 值
/* harmony import */ var _output_dist_index_cmd_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__ = __webpack_require__(/*! ../output/dist/index.cmd.js */ "../output/dist/index.cmd.js");
/* harmony import */ var _output_dist_index_cmd_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0___default = /*#__PURE__*/__webpack_require__.n(_output_dist_index_cmd_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__);
// 加载 index.umd.js 并 读取 其 default 值
/* harmony import */ var _output_dist_index_umd_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_1__ = __webpack_require__(/*! ../output/dist/index.umd.js */ "../output/dist/index.umd.js");
/* harmony import */ var _output_dist_index_umd_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_1___default = /*#__PURE__*/__webpack_require__.n(_output_dist_index_umd_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_1__);
// 加载 index.amd.js 并 读取 其 default 值
/* harmony import */ var _output_dist_index_amd_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_2__ = __webpack_require__(/*! ../output/dist/index.amd.js */ "../output/dist/index.amd.js");
/* harmony import */ var _output_dist_index_amd_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_2___default = /*#__PURE__*/__webpack_require__.n
(_output_dist_index_amd_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_2__);
// 加载 index.cmd2.js 并 读取 其 default 值
/* harmony import */ var _output_dist_index_cmd2_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_3__ = __webpack_require__(/*! ../output/dist/index.cmd2.js */ "../output/dist/index.cmd2.js");
/* harmony import */ var _output_dist_index_cmd2_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_3___default = /*#__PURE__*/__webpack_require__.n(_output_dist_index_cmd2_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_3__);
// 加载 index.var.js 并 读取 其 default 值
/* harmony import */ var _output_dist_index_var_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_4__ = __webpack_require__(/*! ../output/dist/index.var.js */ "../output/dist/index.var.js");
/* harmony import */ var _output_dist_index_var_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_4___default = /*#__PURE__*/__webpack_require__.n(_output_dist_index_var_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_4__);
window.Const1 = _output_dist_index_cmd_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0___default.a
window.Const2 = _output_dist_index_umd_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_1___default.a
window.Const3 = _output_dist_index_amd_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_2___default.a
window.Const4 = _output_dist_index_cmd2_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_3___default.a
window.Const5 = _output_dist_index_var_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_4___default.a
console.log(_output_dist_index_cmd_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0___default.a, _output_dist_index_umd_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_1___default.a, _output_dist_index_amd_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_2___default.a, _output_dist_index_cmd2_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_3___default.a, _output_dist_index_var_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_4___default.a)
console.log(_output_dist_index_cmd_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__["name"], _output_dist_index_umd_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_1__["name"], _output_dist_index_amd_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_2__["name"], _output_dist_index_cmd2_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_3__["name"], _output_dist_index_var_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_4__["name"])
/***/ })
__webpack_require__.n 上文我们就提到了,但是当时我们的例子里没有用到,所以没有解释,这里我们用到了,就来仔细看一下代码。
// getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules
__webpack_require__.n = function(module) {
var getter = module && module.__esModule
// 如果模块拥有 __esModule 属性,即 esModule 模块,那么 import 的时候使用 default 属性
? function getDefault() { return module['default']; }
// 否则,那么 import 的时候使用返回模块的值
: function getModuleExports() { return module; };
__webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter);
return getter;
};
这次我们加载的模块并非 Webpack 本次编译直接从源码里编译得到的,所以对于 Webpack 的这次编译来说,它加载的就是来历不明的第三方代码。Webpack 需要通过 __webpack_require__.n 这样的一个兼容性的函数来处理模块的导入。例子中 commonjs 和 var 都走的都是 non-harmony 的逻辑,其导出的内容都是模块的整体返回值,而非模块的 default 值。
结语
本文从 output 文件的内容分析了 Webpack 对于模块的处理,希望对大家理解 Webpack 模块处理有所帮助。后续我们会继续研究 Webpack 对异步加载和 hot reload 的处理。

